Premium
An insurance premium refers to how much your insurance policy costs, either on a monthly or annual basis.
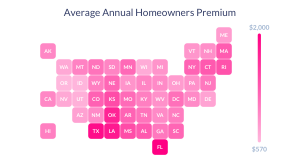
What is an insurance premium?
Insurance premium is a fancy term for the cost of your insurance policy. Usually, insurance companies give you a monthly price, such as $5/month.
To find out how much is renters insurance for your apartment or home (aka your insurance premium), you need to get a quote, which generally requires filling out info online, talking to a customer service representative or underwriter on the phone, or, in Lemonade’s case, chatting with a bot on the Lemonade app or online.
Take note that you may need to pay tax and service fees in addition to your premium, depending on your state and insurance company. Any charges above and beyond the cost of your policy are not the premium.
Insurance premium + tax + service fees = insurance payment
Btw, at Lemonade, we never charge extra tax or service fees- your premium is always the total amount you pay for your insurance policy.
How much does an insurance premium cost?
The cost of your renters or homeowners insurance premium varies and depends on a few factors, such as:
- The type of coverage you choose
- The amount of coverage you choose
- Your personal info and history
- The location of your house or apartment
Let’s dig into this a bit deeper.
The type of coverage you choose
Insurance premiums usually have a base calculation, and different types of insurance coverage have different baseline prices.
Say you’re looking to get renters insurance. Your baseline price will be much lower than someone looking to get homeowners insurance for their house.
Why? Houses tend to cost much more than apartments. Plus home insurance covers the actual structure of your house, while renters insurance only covers your stuff.
The amount of coverage you choose
How much coverage you choose is a big factor. For example, if you own $40,000 worth of stuff and your best friend owns $20,000, your premium will probably be a bit more expensive than hers (depending on other factors).
Similarly, if you choose a $1,000 insurance deductible, and your bestie chooses a $250 deductible, her premium will be more expensive because she’s taking on less risk than you.
Your personal info and history
As you can see, premiums aren’t a one-size-fits-all-model. Your price will ultimately be a reflection of how much risk you present to a potential insurer.
Things like your claims history, the type of home you own, the location of your place, and the condition of your property, among other things, impact the price of your home insurance policy. For example, if you’ve filed homeowners insurance claims in the past, your premium may be a bit more expensive.
Why do insurance premiums go up and down?
The monthly price of your renters or homeowners insurance policy can change for a variety of reasons. Here are some examples:
1. If you filed a claim in the last year, your policy price might increase
2. If you’ve been with your insurer for more than 2 years, your price might decrease thanks to loyalty credit
3. If you’re a homeowner, your price might increase since your home has aged (aka, the ‘Age of Home’ and ‘Renovation Age’ discounts decrease)
How do insurance companies calculate premium?
Traditional insurance companies bring in people called actuaries to manually calculate risk levels and premiums. They calculate how likely you are to file a claim, and how much your claim would likely cost to determine the cost of your premium.
On the other hand, Lemonade’s actuaries use algorithms and bots to instantly price insurance policies. Bonus: AI can actually make your premium lower, since it means less overhead costs to hire several hundred actuaries to price out insurance policies.
How can I get the lowest insurance premium possible?
There are a few things you can do to help lower your premium.
First off, you can install some devices in your home that will help to lower insurance costs. Start with a standard fire alarm and burglar alarm, and you’ve already lowered your risks. And lowered risks equals lowered premiums.
You can also increase your deductible. (Reminder: A deductible is the amount of money you choose when purchasing a policy that will be subtracted from any future claims payouts.) The higher you pay on your deductible, the lower you’ll pay on your premium, and vice versa.
Similarly, you can lower your coverage amounts on your policy. For example, if you decrease your personal property coverage from $30k to $20k, your premium will probably go down a bit. You can update your coverage using Lemonade’s Live Policy whenever you want on the Lemonade app, with no brokers or paperwork involved.
When you’re adjusting your policy to lower your price, make sure to get enough coverage in case something happens to your home or stuff. You won’t want to learn the hard way that you’re underinsured. These guides can help you figure out what is renters insurance and how much homeowners insurance you need.
How often do you pay an insurance premium?
That depends on your insurance company. At Lemonade, our policyholders tend to pay their premium once a month, starting on the date they purchased a policy. For example, if you get insurance on December 5th, you’ll be automatically charged on the 5th of every month!
Lemonaders also have an option to pay on an annual basis- and this is the case with most insurance companies. Some also allow their customers to pay on a semi-annual basis.
What do insurance companies do with insurance premiums?
Traditional insurance companies use premiums to pay out claims, and make a profit by keeping the leftover money they don’t end up using for claims.
Lemonade, though, takes a fixed fee out of premiums, pays reinsurance (and some unavoidable expenses), and uses the rest to pay claims. If there is leftover money, Lemonade uses the unclaimed premiums to donate to charities our community chooses in our annual Giveback.
What’s the difference between insurance rate and premium?
No difference! An insurance rate means the same thing as an insurance premium- it’s the price of your insurance coverage.


